In May 2023, the technical specifications of the SGP.32 (“IoT”) standard for Remote SIM Provisioning were finalised by the GSM Association (GSMA) Working Group 7. This followed the availability of two other standards developed by the GSMA: SGP.02 (“M2M”) and SGP.22 (“Consumer”) introduced in 2014 and 2016, respectively. The availability of SGP.32 has focused the attention of many stakeholders in IoT connectivity on what their approach will be to supporting each, and what the implications are for delivering IoT connectivity.
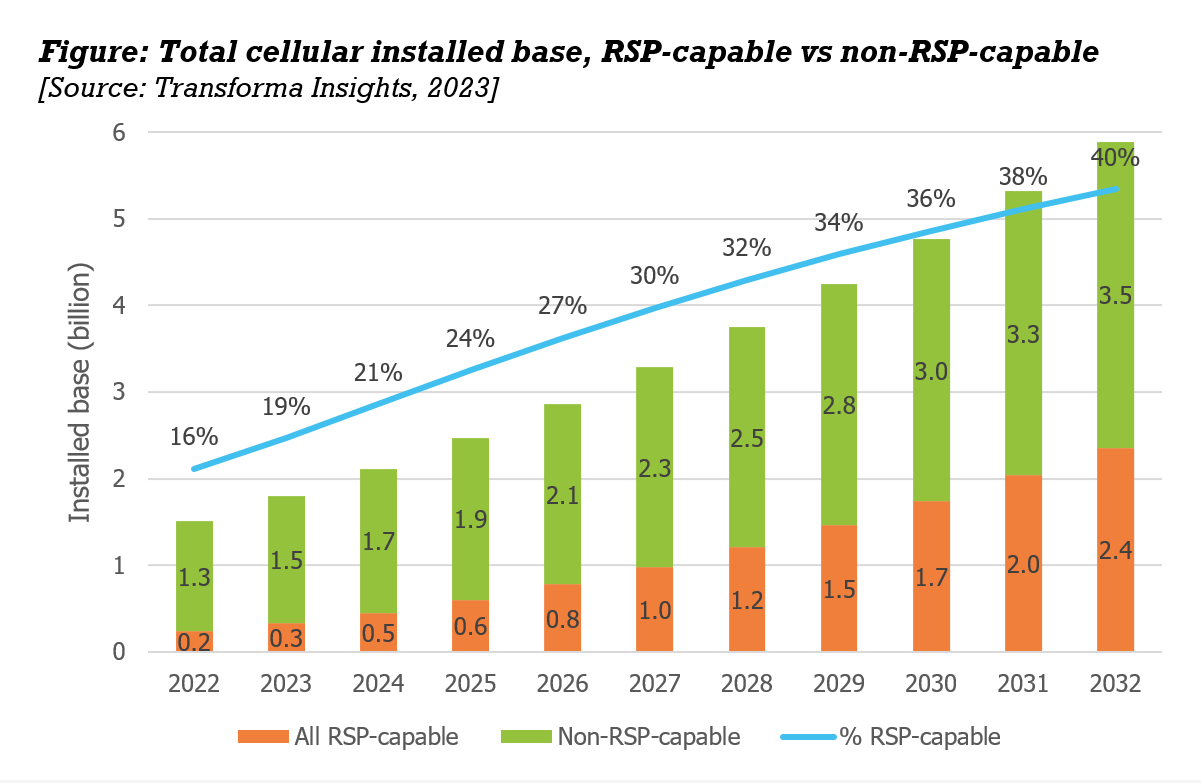
In this report we quantify the cellular IoT market in terms of which approach is taken to Remote SIM Provisioning (RSP), as well as non-RSP-based approaches. The report focuses not just on the use of the GSMA standards, but on all options for connecting cellular-based IoT devices. This also includes non-standard approaches to Remote SIM Provisioning, as well as the well-established non-RSP-based mechanisms such as roaming, multi-IMSI and single IMSI.
Transforma Insights has extensive and highly granular forecasts of the total opportunity for IoT, including cellular-based connections across hundreds of different applications. Considering the sensitivities and deployment circumstances of each application we modelled how cellular-based IoT connections would split between each of the various options for managing SIM profiles. The report includes our view on how annual shipments and installed base split between RSP and non-RSP and which of nine approaches, including the three standards and other options, would account for what proportion of sales and connections between 2022 and 2032.