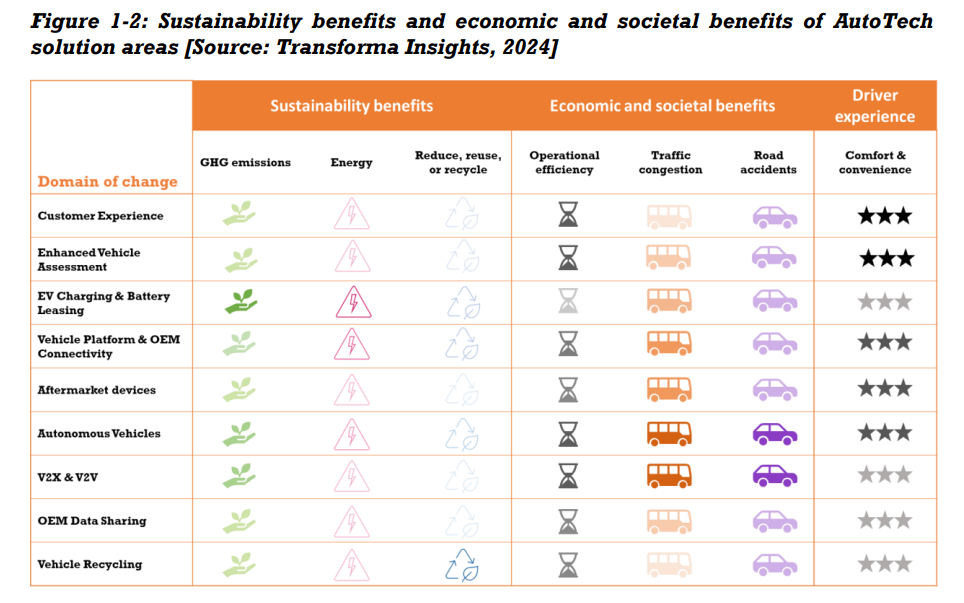
This report examines digital transformation (DX) in the automotive sector, enabled by the key technology groups that are the focus of Transforma Insights’ research. The report focuses on digitally transformative solutions in the automotive industry, encompassing various aspects of the industry, including dealership showrooms, repair and servicing centres, electric vehicle adoption, and the transition towards self-driving vehicles. This report does not address the wider technological changes in the manufacturing of passenger and commercial vehicles or smart mobility and integrated transport systems. The automotive industry has witnessed major disruptions in recent years, affecting all stakeholders in the value chain. Some notable trends include the rapid growth of electric vehicles, the testing and deployment of self-driving cars, and increased investment in digital solutions to enhance customer experience throughout the vehicle ownership lifecycle, from purchasing to usage and servicing. The push towards net-zero emissions and a desire to reduce health risks have driven businesses to adopt electric vehicles and fleets cross multiple industries are being electrified to shift towards a greener transportation to not only reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also lower fuel costs. Rapid digital transformation in the automotive industry has led businesses to innovate and develop mobility for the future, that ensures sustainability, connectivity, safety, and passenger and driver comfort. The battleground has shifted away from product-driven sales and towards technology-based services. Vehicle Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are realising that recurring service revenue is as lucrative if not more so than vehicle sales since the traditional business of selling cars is generally a low margin business. The better margins available for software services is motivating a push by the OEMs towards the software business and some OEMs have entered into joint ventures with technology companies as a part of their strategy to focus on developing connected vehicle software. Data from in-vehicle sensors provides insights into driver and cabin behaviours, enabling OEMs to harness this data to create customised service offerings and unlock new revenue potential. As a result of this, and many other developments, OEMs are integrating high-performance computing chips into vehicles for real-time decision-making, particularly in self-driving cars. The concept of connected vehicles transforms cars into smartphones on wheels, offering an enriched in-vehicle experience. Passengers and drivers in turn are coming to expect an enriched and customised in-vehicle experience, benefitting from automatic adjustments to infotainment, temperature, and lighting settings, along with real-time alerts about road conditions to avoid traffic and potential accidents. Overall, we have identified nine (9) key domains of change in the automotive industry. These are discussed in more detail in this document and comprise: Customer Experience, includes the use of digital technologies to enhance customer experience at customer touchpoints. Enhanced Vehicle Assessment. Includes the use of digital technologies for the service and maintenance of vehicles at repair and service centres. EV Charging & Battery Leasing, includes the use of public and private EV charging, battery swapping, and electrification of roads to support electric vehicles. Vehicle Platform & OEM Connectivity, includes the use of embedded hardware vehicle head units to provide commercial and private vehicles with wide area connectivity and connected and other services. Aftermarket Devices, includes fleet management and a range of other diagnostic, driver support and infotainment devices that are purchased after a vehicle is manufactured and sold to a customer. Autonomous Vehicles, includes autonomous passenger vehicles and autonomous road freight vehicles for reducing the burden on human drivers of strenuous driving requirements. Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) & Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), focuses on vehicle communications with road infrastructure and other vehicles. OEM Data Sharing, includes the sharing of vehicle data across the automotive supply chain. Vehicle Recycling, includes the use of digital technologies in vehicle recycling for maximum utilisation of reusable materials and reduce waste generation to a minimum. Collectively, the concepts listed above will bring significant changes to the automotive sector in the coming years. From a technology perspective and as illustrated in Figure 1 1 below, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Data Sharing (DS), the Internet of Things (IoT), Hyperconnectivity (HC), and Edge Computing (EC) emerge as the key drivers of change in AutoTech. Human Machine Interface (HMI), Distributed Ledger (DL) and Autonomous Robotic Systems (ARS) also contribute to the digital transformation of the automotive sector in selected applications. Figure 1 1: Key technologies enabling digital transformation in AutoTech [Source: Transforma Insights, 2024] AI DS IoT HC EC HMI DL ARS Customer Experience ● ● Enhanced Vehicle Assessment ● ● ● ● ● EV Charging & Battery Leasing ● ● ● ● ● Vehicle Platform & OEM Connectivity ● ● ● ● ● ● Aftermarket Devices ● ● ● ● Autonomous Vehicles ● ● ● ● ● V2X & V2V ● ● ● ● ● OEM Data Sharing ● ● ● Vehicle Recycling ● ● ● The identified nine domains of change have both direct and indirect impacts in terms of economic and societal benefits, and many of them play a vital role in terms of enabling sustainability. As shown in Figure 1 2 below, the greatest sustainability benefits are achieved by implementing EV Charging & Battery Leasing, Autonomous Vehicles, and V2X & V2V. The nine identified doamins have the potential to generate maximum societal and economic benefits by reducing traffic congestion and decreasing road accidents. In terms of driver experience, Vehicle Platform & OEM Connectivity, Aftermarket Devices, Autonomous Vehicles, and Customer Experience have the potential to show maximum benefits.
This report examines digital transformation (DX) in the automotive sector, enabled by the key technology groups that are the focus of Transforma Insights’ research. It covers various aspects of the industry, including dealership showrooms, repair and servicing centres, electric vehicle adoption, and the transition towards self-driving vehicles.
Digital Transformation potential in Automotive
The automotive industry has witnessed major disruptions in recent years, affecting all stakeholders in the value chain. Some notable trends include the rapid growth of electric vehicles deployment, the testing and deployment of self-driving cars, and increased investment in digital solutions to enhance customer experience throughout the vehicle ownership lifecycle, from purchasing to usage and servicing. The push towards net-zero emissions and a desire to reduce health risks have driven businesses to adopt electric vehicles and fleets across multiple industries, which will reduce greenhouse gas emissions and lower fuel costs. Rapid digital transformation in the automotive industry has led businesses to innovate and develop mobility for the future, that ensures sustainability, connectivity, safety, and passenger and driver comfort.
The battleground has shifted away from product-driven sales and towards technology-based services. Vehicle Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) are realising that recurring service revenue is as lucrative (if not more) as vehicle sales, since the traditional business of selling cars is generally a low margin business. The better margins available for software services is motivating OEMs towards the software business and some OEMs have entered into joint ventures with technology companies as a part of their strategy to focus on developing connected vehicle software. Data from in-vehicle sensors provides insights into driver and cabin behaviours, enabling OEMs to harness this data to create customised service offerings and unlock new revenue potential. As a result of this, and many other developments, OEMs are integrating high-performance computing chips into vehicles for real-time decision-making, particularly in self-driving cars.
The concept of connected vehicles transforms cars into smartphones on wheels, offering an enriched in-vehicle experience. Passengers and drivers in turn are coming to expect an enriched and customised in-vehicle experience, benefitting from automatic adjustments to infotainment, temperature, and lighting settings, along with real-time alerts about road conditions to avoid traffic and potential accidents.
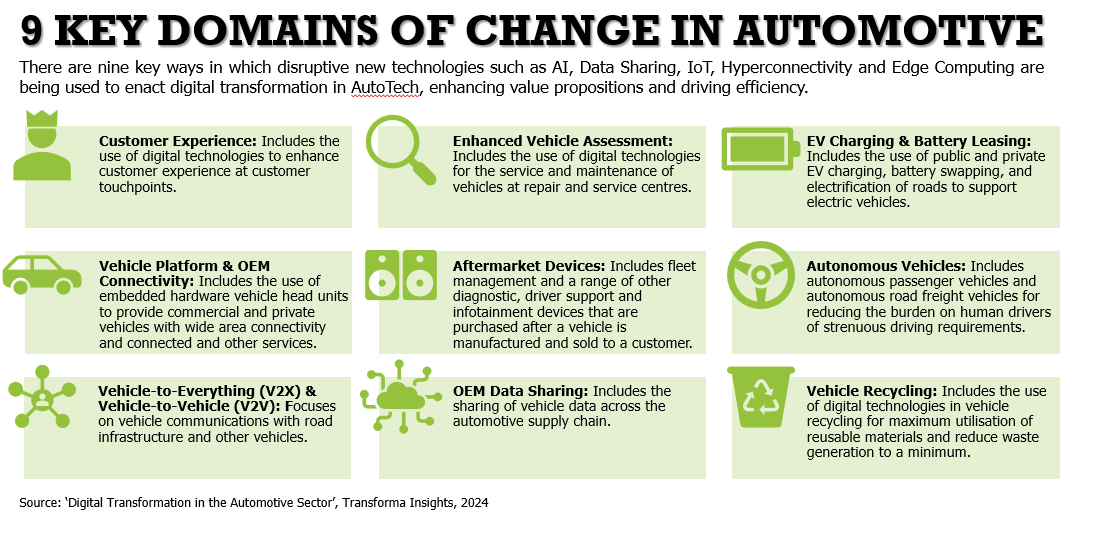
Nine key domains of change in Automotive
Overall, we have identified nine (9) key domains of change in the automotive industry. These are discussed in more detail in this document and comprise:
Customer Experience, includes the use of digital technologies to enhance customer experience at customer touchpoints.
Enhanced Vehicle Assessment. Includes the use of digital technologies for the service and maintenance of vehicles at repair and service centres.
EV Charging & Battery Leasing, includes the use of public and private EV charging, battery swapping, and electrification of roads to support electric vehicles.
Vehicle Platform & OEM Connectivity, includes the use of embedded hardware vehicle head units to provide commercial and private vehicles with wide area connectivity and connected and other services.
Aftermarket Devices, includes fleet management and a range of other diagnostic, driver support and infotainment devices that are purchased after a vehicle is manufactured and sold to a customer.
Autonomous Vehicles, includes autonomous passenger vehicles and autonomous road freight vehicles for reducing the burden on human drivers of strenuous driving requirements.
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) & Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V), focuses on vehicle communications with road infrastructure and other vehicles.
OEM Data Sharing, includes the sharing of vehicle data across the automotive supply chain.
Vehicle Recycling, includes the use of digital technologies in vehicle recycling for maximum utilisation of reusable materials and reduce waste generation to a minimum.
Collectively, the concepts listed above will bring significant changes to the automotive sector in the coming years.
Tracking the impact of 11 digital transformation technologies
This report focusses on digital transformation in the automotive sector as enabled by the key technology groups that are the focus of Transforma Insights’ research. These technology groups include:
3D Printing & Additive Manufacturing
Artificial Intelligence
Autonomous Robotic Systems
Data Sharing
Distributed Ledger
Edge Computing
Future Technologies
Human Machine Interface
Hyperconnectivity
Internet of Things (IoT)
Product Lifecycle Management
Robotic Process Automation
Clearly, not all of these technology groups are directly relevant to AutoTech, but many of them are highly relevant (including IoT, Artificial Intelligence, Edge Computing, Data Sharing, and others).
Accordingly, the aim of this document is not to chart the future direction of the automotive industry as a whole, but to highlight the key areas of change that are enabled by new and
emerging technologies. The bulk of this report (Section 4) discusses these key domains of
change and includes an overview of each together with a discussion of key benefits and an
analysis of key vendors. We also identify key enabling technologies for each domain of change (from the list above) and provide summary details of illustrative case studies that are available in Transforma Insights’ Best Practice & Vendor Selection database.
The purpose of the document is two-fold. First, from the perspective of those in the
automotive industry and related areas (such as city administrations, vehicle fleet operators,
and so on), the document highlights new and emerging aspects of change that will have an
impact in the next few years. Second, from the perspective of potential vendors to the
AutoTech space, it highlights the key emerging areas of opportunity to sell new products,
services, and solutions. Our analysis of the key technologies that enable each of the identified areas of digital transformation will help vendors of horizontal (technology-specific) capabilities identify the contexts in which they may secure new business opportunities.
Specific exclusions from the scope of this report include smart mobility (which has been covered in Bike & Scooter Sharing), intergrated transport systems (separately discussed in Digital Transformation in Smart Cities), unmanned non-road vehicles (dealt in a separate report titled, Unmanned Non-Road Vehicles), and vehicle rental, leasing, and sharing (which has been separately explored in Vehicle Rental, Leasing & Sharing Management).
If you have any questions about the content of this report or would like to speak with the author or any other analysts on any topic, you can make use of our Analyst Enquiries service by emailing enquiries@transforminsights.com.