This comprehensive report focuses on the sustainability benefits of a range of digital transformation (DX) solutions, and related ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) benefits. It identifies the 'Clean Dozen' solution areas including smart buildings, supply chain and remote monitoring, which will have the greatest impact.
This 112-page report focuses on the sustainability benefits of a range of digital transformation (DX) solutions, and related ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) benefits. The solutions profiled in this report have been defined to include all of the most impactful sustainability-enabling applications that Transforma Insights has previously identified through a comprehensive market review of all emerging digital transformation Use Cases. These have been aggregated into ‘Solution Areas’ that are groups of related concepts defined with the intention of better-informing specific groups of end-user and also vendors who might be in conversation with those end-users.
Overall, we have identified twelve key areas (the ‘Clean Dozen’) where digital transformation can significantly help an organisation achieve sustainability goals. These are discussed in more detail in this document and comprise:
Fleet Operations, including a range of applications associated with the efficient operation and maintenance of vehicle fleets.
Supply Chain includes a range of applications used to improve the working and efficiency of supply chain operations such as sourcing, logistics, transportation, warehousing, manufacturing and production.
Smart Cities comprises of wide spectrum of smart city applications ranging from street lighting control to traffic management and parking space monitoring.
Smart Public Transport, solutions that enable tracking of buses, assets that are part of sharing schemes (such as bikes, e-scooters, cars).
Smart Buildings, technologies used to monitor and control the uses of resources (such as electricity, heating, cooling, water) in a building.
Smart Grid, including all aspects of grid operations, energy generation, smart metering, transmission and distribution.
Campus Microgrids refers to a network of distributed energy resources (DERs) for managing electricity flow in a campus location.
Remote Monitoring & Maintenance includes a range of applications for remote monitoring and maintaining the condition of machines.
Smart Healthcare, solutions used to remotely monitor the health of people.
Drone-based Solutions, solutions that enable efficient maintenance and monitoring of infrastructure in buildings, wind farms with drone-based inspection.
Smart Agriculture includes a range of applications used to make farming methods more efficient while increasing yield.
Efficient Operations, other technology use cases that contribute towards sustainability initiatives but that are not related to IoT.
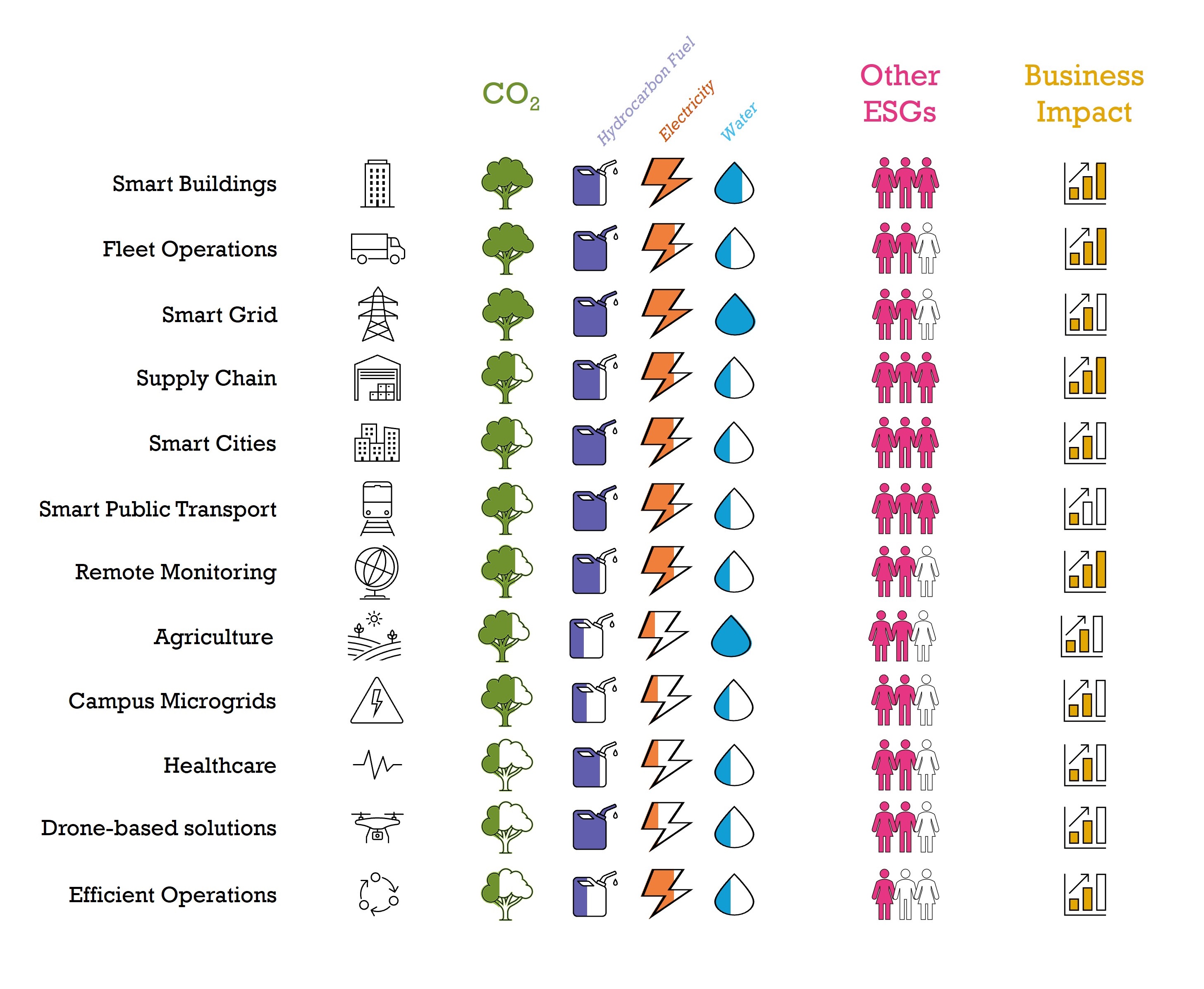
For each of the twelve focus areas listed above the report includes:
Identification of case studies and reported findings of relevant real-world solutions in terms of their impact on electricity consumption, (hydrocarbon) fuel consumption, water consumption, and CO2 emissions.
The identification of wider ESG (Environmental, Sustainability, and Governance) benefits such as the potential for fleet management solutions to reduce speeding and so accident rates, or for supply chain monitoring solutions to help manage the provenance of raw materials or parts.
The business impact of identified applications, including financial costs saved and potentially incremental revenues.
Illustrative scenarios to aid dialogue between vendors and potential end-user adopter.
Discussion of key supporting technologies.
A sample extract of this report (covering Smart Buildings) is available to free 'Essential' subscribers: Sustainability enabled by Digital Transformation [Sample: Smart Buildings]